Related Links
Cyperus granitophilus (granite flat sedge) Discovered in Texas
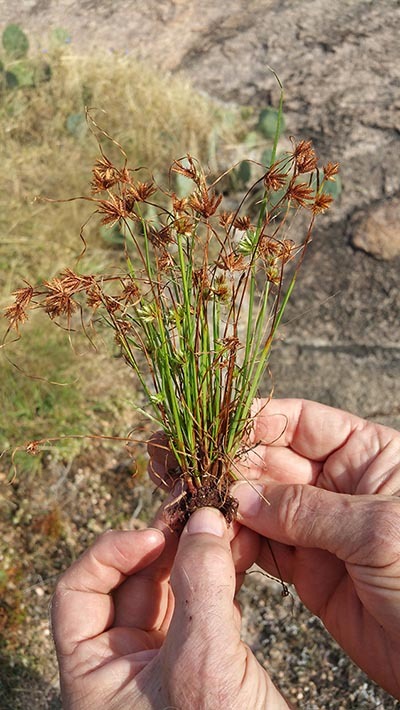

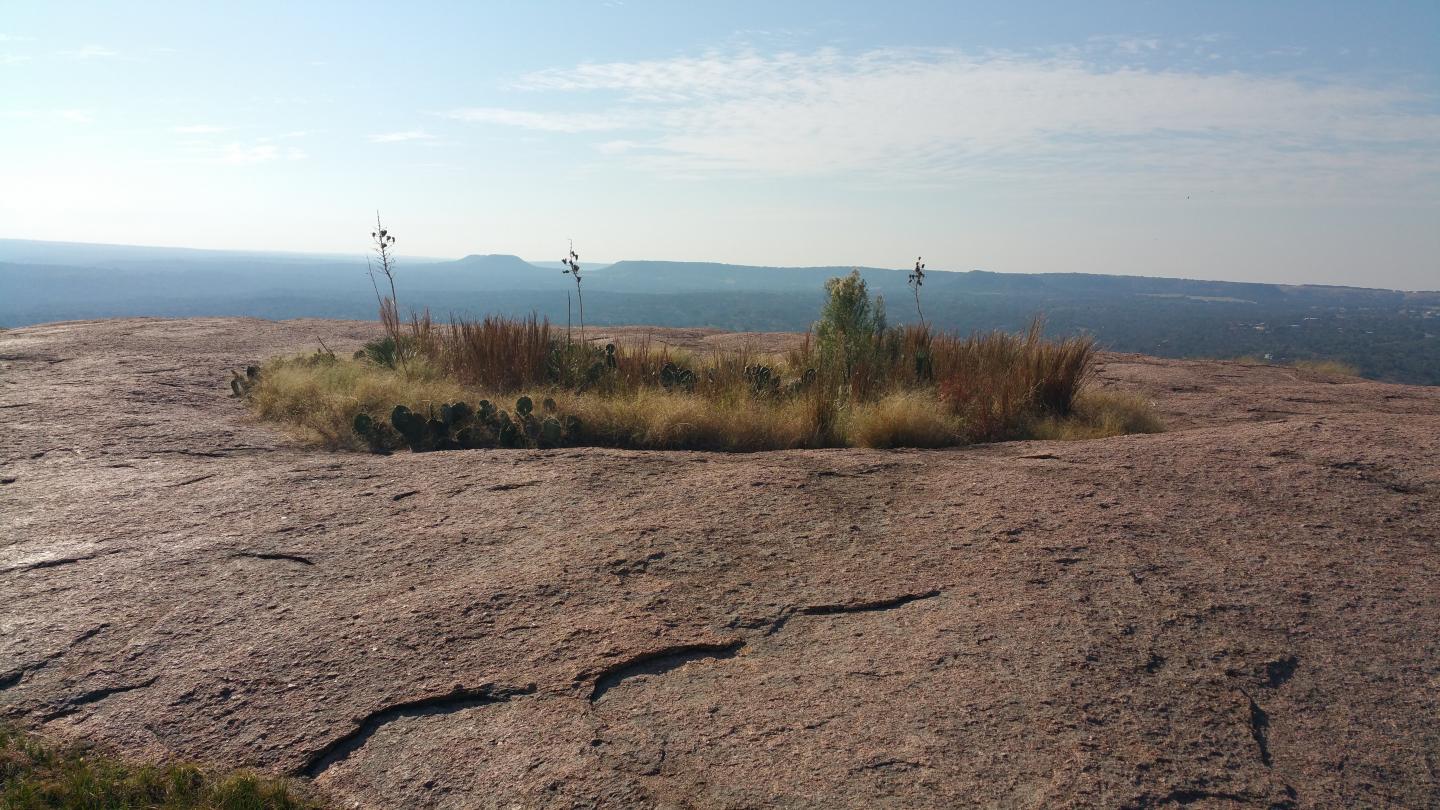
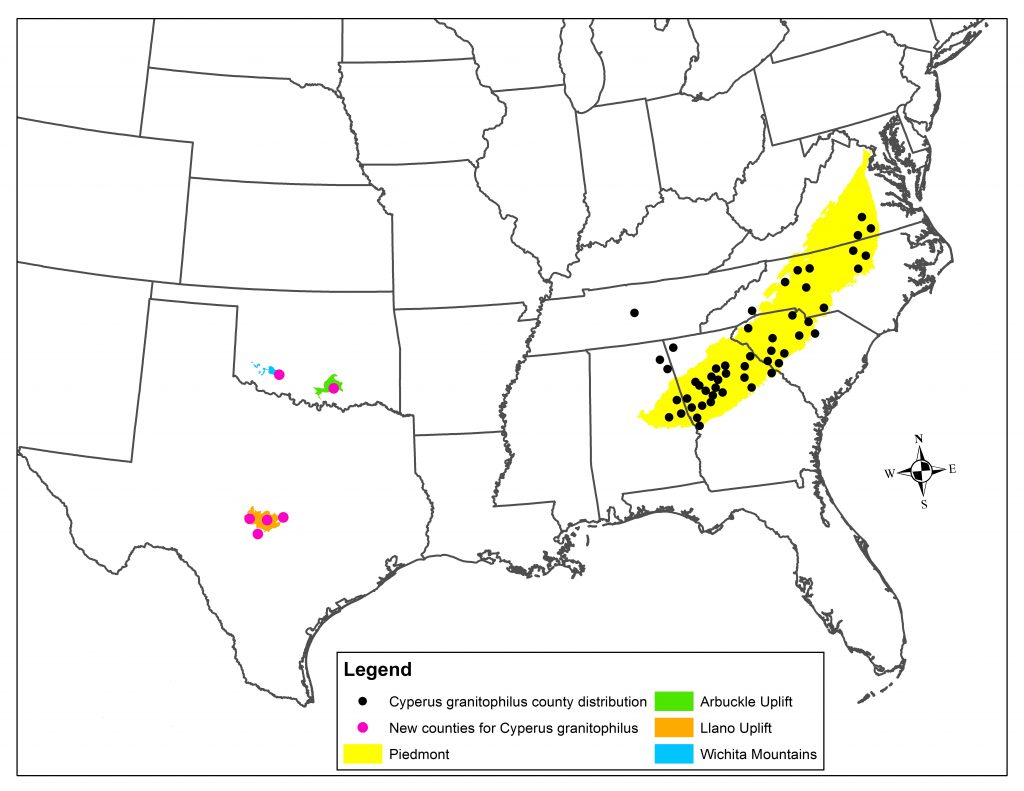
During the course of the flora of Enchanted Rock project, several interesting species were found. One species of note is Cyperus granitophilus (granite flat sedge). This species is a member of the sedge family (Cyperaceae) that is known to occur in the Piedmont granite regions of Georgia, Alabama, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia. This species only grows on granite outcrops. While conducting field work for the flora of Enchanted Rock, Bob O’Kennon and Kim Taylor discovered a sedge that they did not recognize. They collected the plant and later identified it as Cyperus granitophilus. This represented the first time this plant had knowingly been collected in the state of Texas, some 790 miles from its known range in the Southeastern United States.
After discovering the species, Bob and Kim set out to determine its true distribution. In order to do this, they examined herbarium specimens of a closely related species, Cyperus squarrosus. This species looks very similar to C. granitophilus. They examined herbarium specimens from the BRIT herbarium, the University of Texas, Texas A & M University, and the University of Oklahoma, and discovered that several of the specimens were actually Cyperus granitophilus plants that had been mis-identified as C. squarrosus. A total of 27 collections from Texas and 11 collections from Oklahoma were actually Cyperus granitophilus. This means that the true range of Cyperus granitophilus includes both Texas and Oklahoma. All of the specimens of C. granitophilus were found growing on granite outcrops similar to the granite outcrops where the plant is found in the southeastern U.S. Bob and Kim submitted their findings to the Journal of the Botanical Research Institute of Texas and the paper was published in July, 2015.
CITATION: O’Kennon, R.J. & K. Taylor. 2015. Cyperus granitophilus (Cyperaceae), a granite outcrop endemic, new for Texas and Oklahoma (U.S.A.). J. Bot. Res. Inst. Texas 9:251–257.